Casting Defects
Defects in casting reduce the performance of cast component and not desirable. Caster has to supply components as per quality specification from the customers.
Casting defects occur during
- Flow of molten metal in the die / mold cavity
- Heat transfer (loss of heat during the flow of melt)
- Solidification (cooling after the die cavity is completely filled)
Using computer simulation of metal casting process, accurate prediction of the casting defects is possible.
Aganita has assisted foundries and casting companies towards prediction of casting defects using simulation software ADSTEFAN
Major casting defects are
Flow related defects
- Cold shut, Cold laps
- Misrun
- Blow hole
- Sand erosion/inclusion / Die erosion
- Slag/ Oxide entrapment
Solidification related defects
- Shrinkage Porosity (Macro & Micro)
- After machining porosity
Stress related defects
- Cracks
- Hot tear
- Distortion (casting & core)
- Contraction
Core gas related defects
Air EntrapmentPotential Air Entrapment Zone Predicted
Above figure demonstrates defect mapping of blow holes defects of ADSTEFAN simulation vs actual defect location in sand casting process. Root cause of defect is identified as air pocket isolation are observed in casting in ADSTEFAN results. Due to this air pocket isolation is observed in cavity which leads air gets entrapped between the molten metal and thus forms as Gas porosity casting defect and same phenomenon is observed in shop floor trails.
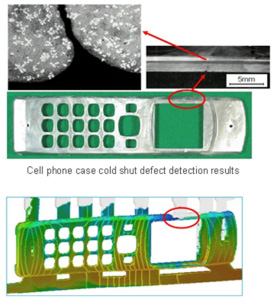
Cold Shut/ Cold lap
Cold shut/ Cold Lap casting defect refers to a type of casting defect that occurs when molten metal does not properly fuse together during the casting process. When molten metal enters the mold from two gates, the streams will meet at a junction. Low Temperatures can prevent fusion at the junction, causing the streams to solidify before fusion, creating a cold shut defect in casting.
Above images are comparison between casting simulation ADSTEFAN Simulation results with actual cold shut casting defect. As observed , there is a temperature drop in highlighted region due to improper fusion of molten metal from different ingates during filling. Due to temperature drop, cold shut defect is formed in casting. In ADSTEFAN, one can measure temperatures in any place at any point of time during mold filling. Thus, gives gating designer a complete idea of temperature variation of molten metal during pouring and can predict cold shut defect in casting well before pattern is even made. Thus, it saves energy, production cost and development lead time.
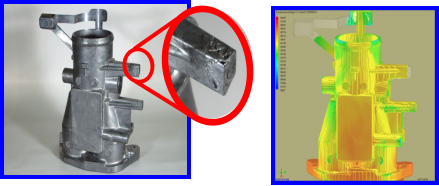
Hot tear
Hot tear defect in casting occurs predominantly due to tensile residual stresses that occur in casting during the cooling period. Embrittlement in castings enhance the hot tear formation. Using ADSTEFAN for casting simulation, designer can predict the extent of residual stresses induced in the casting and explore the probability of hot tear formation.
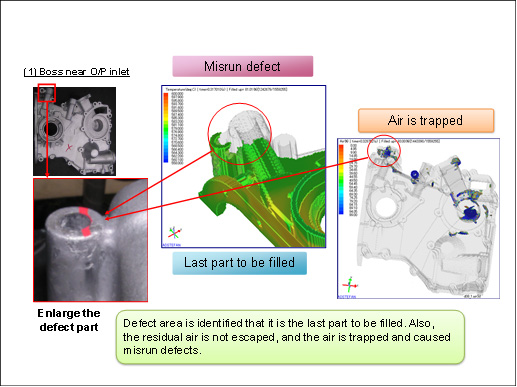
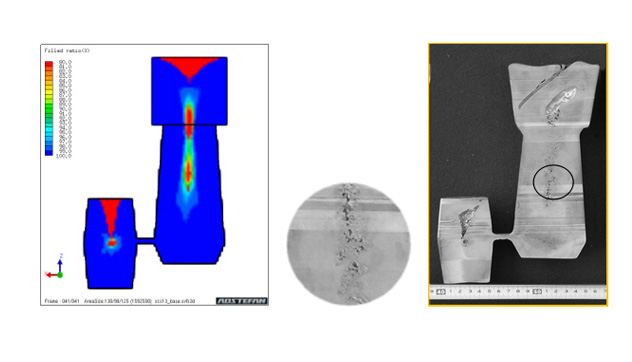
Misrun
Mis run is a casting defect that occurs when the molten metal losses heat, and temperature has been reduced to such a level, it can not flow further to fill the mold cavity.
Figure Above shows the misrun defect occurring in the cast component (left side), and formation of the misrun defect by casting simulation using ADSTEFAN.
Figure above shows misrun defect predicted by ADSTEFAN simulations, and also regions off air entrapment defect. Figure compares the simulation results with plant trial castings.
- Sand inclusion
Sand inclusion casting defects, also known as sand inclusions or sand blow, are common casting defects in sand casting processes. It occurs when loose sand particles become trapped in molten metal and subsequently solidify within the casting. Sand inclusions casting defect can compromise the integrity and surface finish of the casting, leading to rejecting parts and increased production costs.
Above figure demonstrates defect mapping of inclusion casting defect for sand casting process with ADSTEFAN simulation software results. Root cause of defect is identified as high velocities at casting region in ADSTEFAN results. Due to this higher filling velocities turbulence is observed in cavity which leads to sand inclusion defect in casting and same phenomenon is observed in shop floor trails.
Slag inclusion:
Slag inclusion defect is one of common casting defects in sand casting process particularly when casting ferrous metals. Slag inclusion defects in casting are mainly formed due to improper molten metal flow inside mold cavity.
More chances of slag inclusion occur due to low temperatures and more contact time with oxygen that is present in environment and mold. More time metal is exposed to oxygen, more slag is formed by converting in molten metal into oxide form
Above figure demonstrates air contact time of molten metal inside cavity for sand casting process In ADSTEFAN casting simulation software. Higher contact time with molten metal and air, higher chances of slag inclusion in casting. Design engineer can also validate temperature distribution and filling velocity of molten metal during filling of mold cavity.
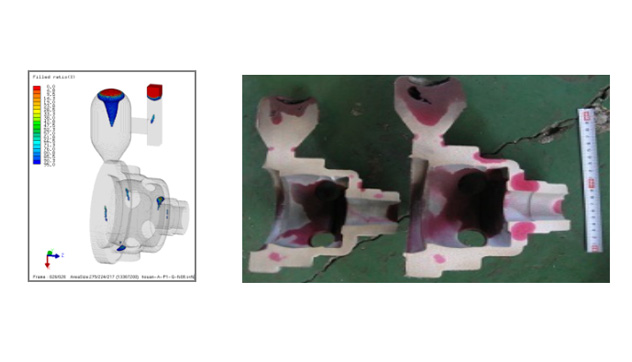
Shrinkage Porosity
As the molten metal solidifies, it undergoes volume reduction due to solidification shrinkage. If there is insufficient molten metal available to compensate for this shrinkage, voids or pores form within the casting as casting defects.
The location of shrinkage porosity casting defect can vary depending on factors such as the casting geometry, gating system design, and cooling rate. Common locations include thick sections, corners, and areas farthest from the risers
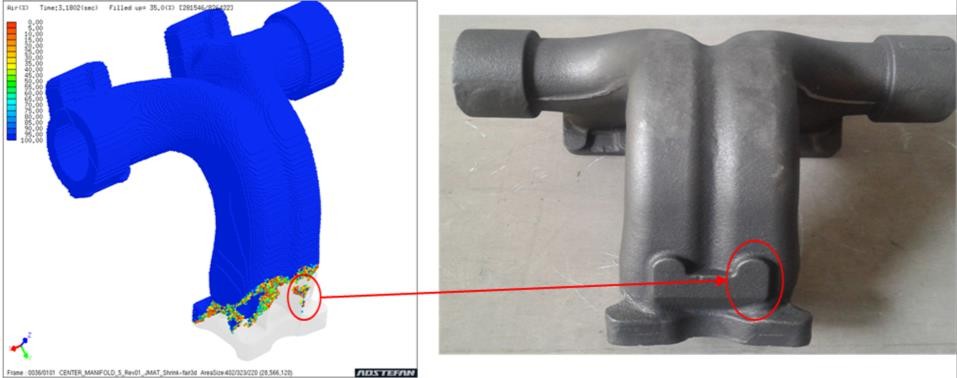
Above figure demonstrates defect mapping of shrinkage porosity casting defect for sand casting process with ADSTEFAN simulation software results. Root cause of defect is identified as isolation during solidification are observed in casting in ADSTEFAN results. Due to this isolation during solidification is observed in cavity which leads Shrinkage porosity in casting and same phenomenon is observed in shop floor trails. .
Above figure demonstrates defect mapping of shrinkage porosity casting defect for sand casting process with ADSTEFAN simulation software results. Due to isolation during solidification in cavity leading to Shrinkage porosity in casting and same phenomenon is observed in shop floor trails.
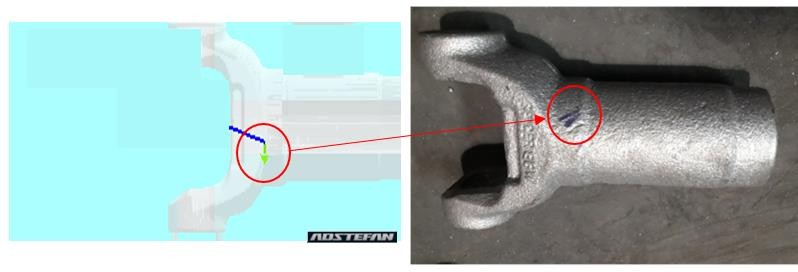
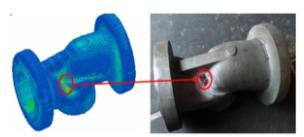
Crack defect:
Crack is one of the most critical and costly defects in sand casting. It can lead to product failure, increased scrap rates, and production delays.
Defect mapping of crack defect in sand casting process for actual and ADSTEFAN simulation results are displayed in above figure. Observed crack defect during shop floor trials which is highlighted in above figure right hand side where Dye Penetration test is performed to determine crack location. Root cause of defect is identified as high stress concentration at crack location observed in casting in ADSTEFAN results. Due to this high stress development at highlighted location , cracks defect is formed in casting and same phenomenon is observed in shop floor trials.