Types of Cooling Lines and Thermal balancing die casting Using ADSTEFAN Casting Simulation Software for Casting gating optimisation & Cooling lines optimization
Introduction:
Die casting is substantially a thermal process where great heat energy is required to superheat the casting alloy into the liquid state with the desired viscosity and solidify to attain desired shape. Die insert is an important component of the dies commonly used in die casting processes. Die casting dies are subjected to various thermal and mechanical loads. Maintaining dies at optimum thermal management is very critical and this can be achieved by cooling/ heating lines in dies. Heat cracking, die soldering and erosion are some of the most relevant phenomena that shorten dies lifetimes. Each insert has at least one simple cooling channel for controlling the thermal state of the mold and for cooling every hot spot efficiently.
Benefits of Cooling system:
- Decrease Cycle time – Through targeted heat dissipation, exactly where the heat is generated and reduce cycle time and increase productivity
- Porosity and Shrinkage Control – Optimal temperature control of the material flow
- Homogeneous, Optimal Microstructure Formation – By achieving thermal equilibrium throughout casting with help of thermal temperature control
- Reduction of rejection rates by improving casting quality
- Reduction of scrap and maintenance costs
- Less Maintenance time
Types of cooling lines:

Types of Cooling Media:
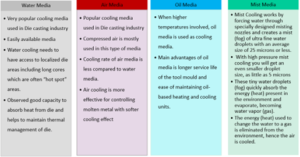
Case Study – Effect of Cooling Type on Die Temperature using ADSTEFAN Simulation Software:
To study different cooling type effect on die temperature, we have taken casting part as shown in figure of material ADC 10, Pouring Temperature of metal – 710°c, Die Material – H 13 and Die temperature as 200°c.
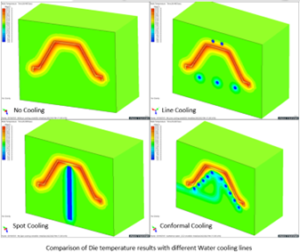
We are taking Line cooling, spot cooling and conformal cooling system for sample casting. Cooling media considered in all cases is Water. The temperature of water is considered 30°C
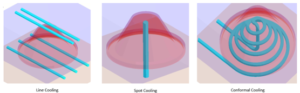
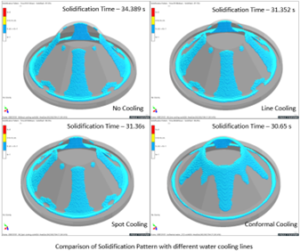
Comparison analysis for Water cooling media:
- Observed more solidification time for casting without cooling lines and with conformal cooling, less solidification time is observed.
- Rapid cooling of casting is observed in conformal cooling compared to line and spot cooling type.
- Uniform solidification of casting is observed in conformal cooling case study as cooling is acting on casting uniformly.
- Conformal cooling is effective compared to other cooling lines as rate of heat extraction is more.
- Spot cooling is effective only at spot near to casting.
Conclusion:
The study demonstrates that effective cooling line design and thermal balancing in die casting, when supported by ADSTEFAN Casting Simulation Software, play a vital role in improving overall casting quality. By simulating various casting methoding and process parameters, engineers can achieve casting gating optimisation and cooling lines optimization, leading to uniform temperature distribution and reduced thermal stresses. This approach minimizes casting defects such as shrinkage porosity, hot spots, and warpage, thereby ensuring improved dimensional accuracy and surface finish.
Furthermore, integrating casting methoding and gating optimization with thermal balancing strategies significantly lowers casting rejection rates on the shop floor. The combination of advanced simulation, accurate prediction, and optimized cooling design provides a cost-effective way to enhance productivity, extend die life, and ensure consistent part quality. As industries strive for higher efficiency and casting rejection reduction, the use of ADSTEFAN for gating and cooling optimization proves to be an indispensable tool for achieving reliable and defect-free die castings.
Recent Posts
- LPDC simulation of alloy wheel to predict the defects produced due to improper die heating.
- Implementing Machine learning on Defect prediction for Investment casting through ADSTEFAN casting simulation software
- Methods for Indian Casting Manufacturers to Overcome Fluctuating Raw material price
- Casting rejection can be controlled, Here are important tips
- Die Casting 4.0 – Casting Defect Prediction by Machine Learning for Die casting industries using Casting Simulation Software
- Types of Cooling Lines and Thermal balancing die casting Using ADSTEFAN Casting Simulation Software for Casting gating optimisation & Cooling lines optimization
- Yes! We can perform air entrapment prediction and overcome by air entrapment simulation using ADSTEFAN casting simulation software. Here is how we can do
- Are You Facing Challenges in Utilizing Casting Simulation Software? Here’s How to Overcome Them
- Better practice for effective utilization of simulation software
- More Yield, Fewer Defects – How ADSTEFAN helps to Transforms Gating Design! – Case study on Steel Valve body castings