Gas Porosity Casting Defect in Sand Casting
Blow holes/ Gas porosity casting defect refer to voids or cavities within the metal casting caused by the entrapment of gases, such as air or steam, during the solidification process. These voids may range in size from tiny pores to larger cavities and can adversely affect the mechanical properties, surface finish, and overall quality of the casting. Blow holes casting defect can vary in size and shape and may be distributed throughout the casting or concentrated in specific areas.

A.Gas Porosity Casting Defect
Root Causes of Blow holes casting defect:
- Improper Venting: Inadequate venting in the mold prevents gases from escaping, leading to their entrapment in the casting.
- High Pouring Temperature: High pouring temperatures can cause increased gas solubility in the molten metal, leading to gas evolution during solidification.
- Turbulence filling: Turbulence filling of molten metal in cavity will lead to more air entrapment within molten metal which leads to blow holes defect in casting.
- Improper Gating Design: Poor gating design can lead to trapped air which can result in gas porosity.
Remedies for Blow holes casting defect:
- Effective Venting: Design molds with sufficient vents to allow gases to escape easily during pouring and solidification. Proper gating and riser design can also help in venting.
- Optimized Pouring Temperature: Control the pouring temperature based on the alloy being cast. Lowering the pouring temperature can reduce gas solubility and minimize gas evolution.
- Metal Degassing: Implement metal degassing techniques such as using degassing agents or employing vacuum or inert gas processes to remove dissolved gases from the molten metal.
- Use of Inert Gases: Inert gases like nitrogen or argon can be used to create an inert atmosphere around the mold, reducing the likelihood of gas absorption during pouring.
- Process Control and Monitoring: Implement strict process control measures and regularly monitor parameters such as temperature, moisture content, and gas levels to identify and rectify issues promptly.
Through using casting simulation tools such as ADSTEFAN – Hitachi ICS – Japan based casting simulation software, Design engineer can understand air entrapment prediction by access air evacuation pattern during filling of molten metal inside mold cavity and check if any air pocket isolation is forming during filling of metal inside mold cavity. This early casting defect prediction helps design team to gating optimization and reiterate simulations by modifying gating design and providing vents are air trapped location and overcome blow holes casting defect.
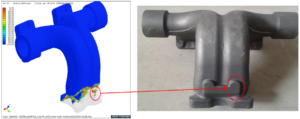
b. Defect mapping for Blow holes defect between ADSTEFAN results and Shop floor trails
Above figure(b) demonstrates defect mapping of blow holes casting defect for sand casting simulation process with ADSTEFAN casting mold flow simulation results for air entrapment simulation. Root cause of defect is identified as air pocket isolation are observed in casting in ADSTEFAN results. Due to this air pocket isolation is observed in cavity which leads air gets entrapped between the molten metal and thus forms as Gas porosity casting defect and same phenomenon is observed in shop floor trails.
Preventive action taken on component by modifying gating design to provide proper air vents are air pocket isolated and thus blow holes casting defect is controlled. This optimization is carried out in ADSTEFAN software and best gating design, and vent locations are considered in shop floor trails thus leading to elimination of blow holes defect in shop floor. By performing corrective actions using ADSTEFAN simulation software , we are able to reduce shop floor trails, production, and development time of component.
Recent Posts
- LPDC simulation of alloy wheel to predict the defects produced due to improper die heating.
- Implementing Machine learning on Defect prediction for Investment casting through ADSTEFAN casting simulation software
- Methods for Indian Casting Manufacturers to Overcome Fluctuating Raw material price
- Casting rejection can be controlled, Here are important tips
- Die Casting 4.0 – Casting Defect Prediction by Machine Learning for Die casting industries using Casting Simulation Software
- Types of Cooling Lines and Thermal balancing die casting Using ADSTEFAN Casting Simulation Software for Casting gating optimisation & Cooling lines optimization
- Yes! We can perform air entrapment prediction and overcome by air entrapment simulation using ADSTEFAN casting simulation software. Here is how we can do
- Are You Facing Challenges in Utilizing Casting Simulation Software? Here’s How to Overcome Them
- Better practice for effective utilization of simulation software
- More Yield, Fewer Defects – How ADSTEFAN helps to Transforms Gating Design! – Case study on Steel Valve body castings